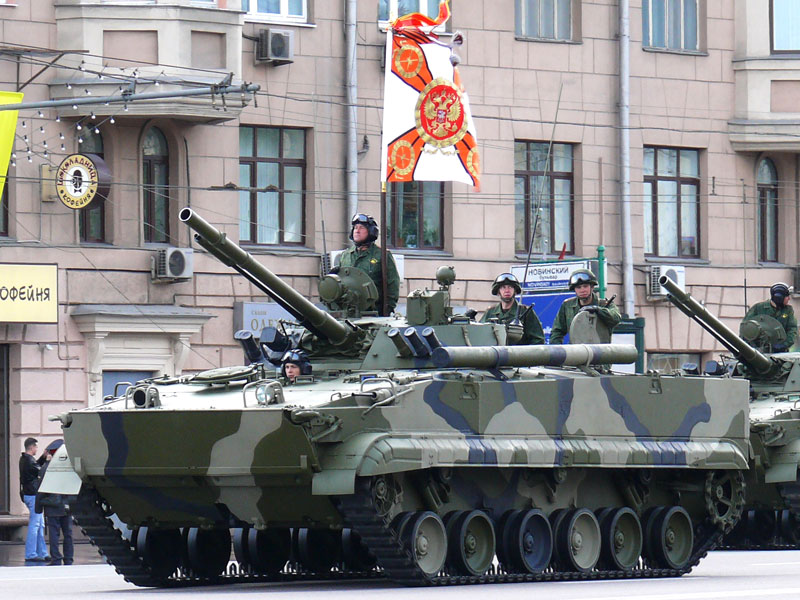
The BMP-3 vehicles are part of a Venezuelan program to modernize its armed forces. Other purchases include the Su-30 fighter aircraft, and the local manufacture of AK-103 assault rifles.
In 2010, Venezuela received a $2.2 billion loan from Russia for the purchase of 92 T-72M1M main battle tanks, BTR-30 armored personnel carriers and artillery systems.
Venezuela is projected by Russia to become its second largest market for arms purchases after 2015. Only India would be a bigger market and surpassing China.
The BMP-3 is an amphibious, tracked Infantry Fighting Vehicle with several variations developed by the Tula Design Bureau for Instrument Engineering. The specifications of the basic version are:
- a crew of 3
- a length of 7.1 m
- a width of 3.2 m
- a height of 2.4 m
- a weight of 18.7 tons
- a range of 700 km
- a road speed of 72 km/hr
- an offroad speed of 45 km/hr
- a speed of 10 km/hr in the water
The crew of the BMP-3 consists of a driver, gunner and commander and can carry between 7 to 9 passengers. The vehicle provides NBC protection for the crew and can be fitted with reactive armor.
The BMP-3 is one of the most heavily armed IFV around. The turret is fitted with a 100 mm 2A70 low-velocity rifled gun, 30 mm 2A72 gun and 7.62 mm coaxial gun. There are usually two 30 mm machine guns at the front of the chassis.
The 100 mm gun can fire the 9M117 / AT-10 Stabber laser beam-riding anti-tank missiles. There are also grenade launchers and all weapons can be fired when the vehicle is stationary, afloat or on the move.
Depending on the BMP-3 version, the vehicle can be fitted with an automatic fire control system, including a laser range-finder, an optical sight and thermal imaging sight. The Shtora or Arena counter-measures systems may also be fitted.
http://en.rian.ru/world/20130328/180309221/Venezuela-Receives-13-Russian-Armored-Vehicles.html